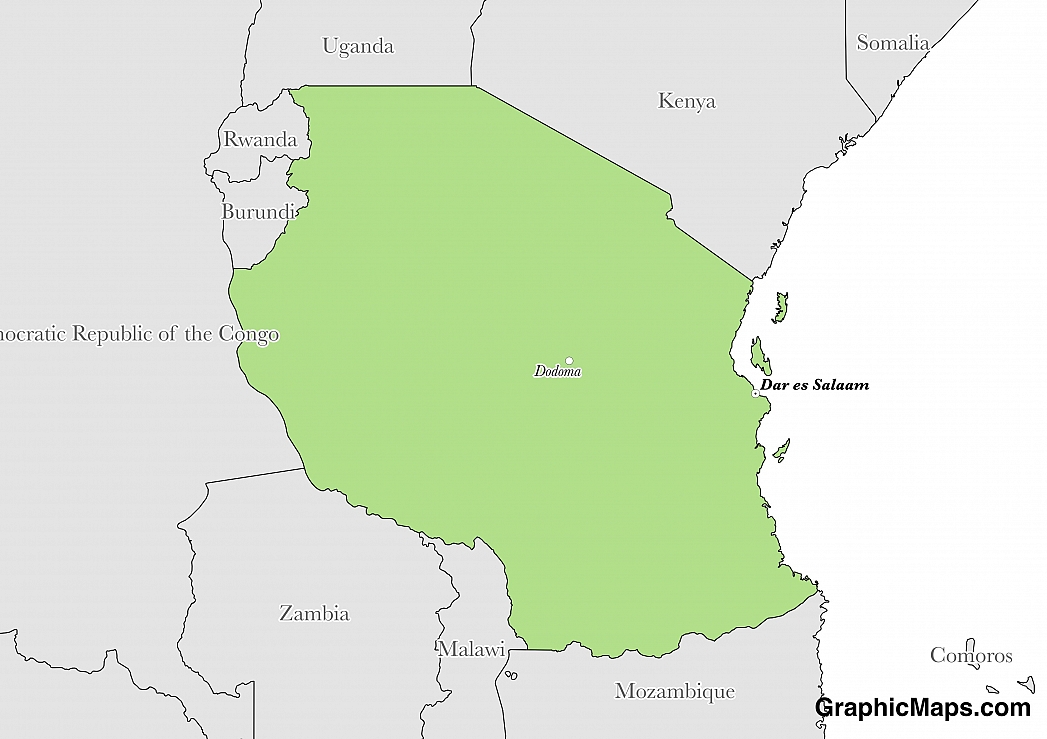
The official language of Tanzania is Swahili, although the country is considered multilingual. Swahili belongs to the Bantu subgroup of the Niger-Congo language family. In Tanzania, it serves as one of the major languages of business, together with English. This language may be written by using one of two alphabets: Latin or Arabic. The Latin alphabet is the same used by the English language. The Arabic alphabet is different in that it is written from right to left in a cursive-like script.
The population of Tanzania is estimated at 52.483 million. Of these individuals, 47 million speak Swahili. This language is used by the government, public schools, and major media channels. The English language, which was first introduced by colonial powers, is spoken and understood by approximately 4 million people. English speakers in Tanzania tend to have a higher level of education and economic resources than non-English speakers. One of the most widely spoken native languages here is Sukuma, which is spoken by approximately 7.3 million individuals throughout the Geita, Mwanza, and Shinyanga regions.
Given that Swahili is the most widely spoken language in the country, learning a few phrases is crucial for anyone planning a trip to Tanzania. Some basic phrases include: “hello” (jambo), “thank you very much” (asante sana), “how are you” (habari), “good” (nzuri), and “what is your name” (jina lako nani). A very common and slightly less formal greeting is “mambo”, to which visitors may reply either “poa” or “safi” (both of which mean “cool”).
As a multilingual country, Tanzania is home to many minority languages. One of these minority language groups is known as Khoisan, which is not classified within an African language family. Khoisan languages are unique in that they are expressed by a number of clicking sounds. The two Khoisan languages heard in Tanzania include Sandawe and Hadza. Sandawe is concentrated around the Dodoma area and has around 65,000 native speakers. Hadza is concentrated around Lake Eyasi and has around 1,000 native speakers. Native Hadza speakers belong to the Hadza people, recognized as the only remaining hunter-gatherer society in Tanzania.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
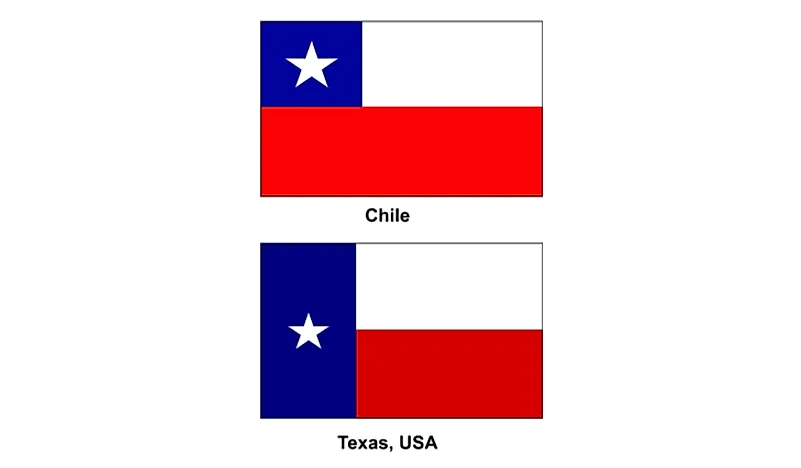
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20