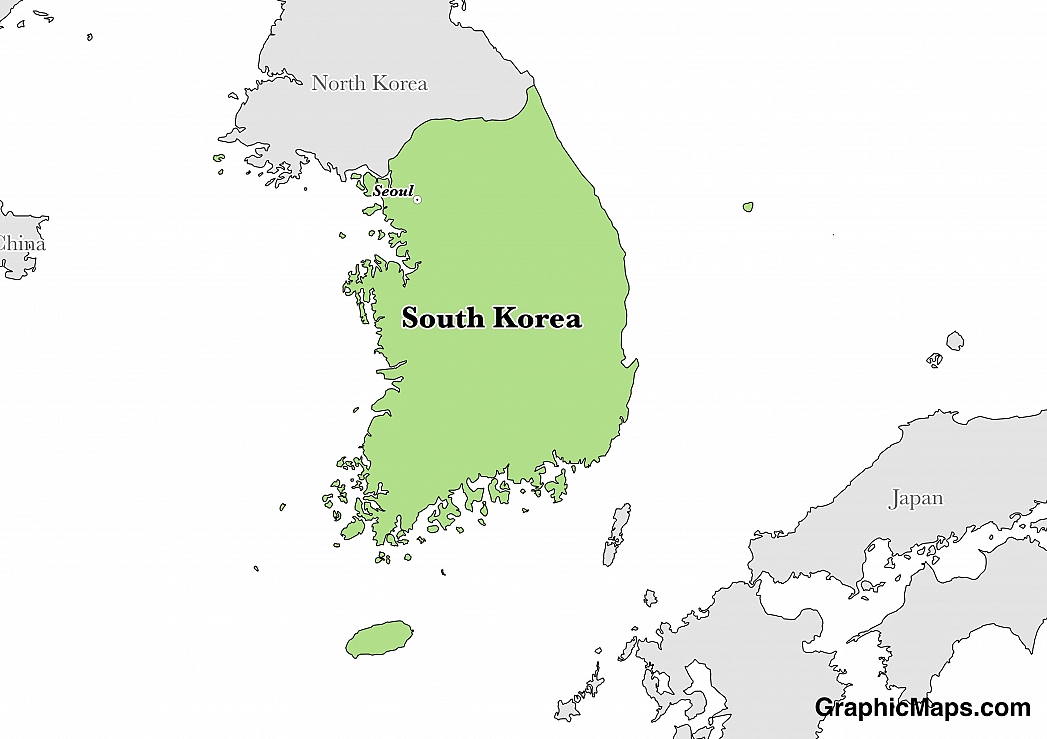
In the Republic of Korea (South Korea), the national and official language is Korean. There are about 80 million people around the world who can speak Korean. Although still debatable, it is thought that Korean language belongs to the Altaic family a macro-family that also includes the Tungusic, Mongolian, and the Turkic families. During the occupation of Korea in the Middle Ages, the Chinese introduced their characters that were incorporated in Korean writing which came to be known as Hanja. Later on, with the invasion and control of the Japanese, the script was changed to include Japanese characters and was called Hangul. The Korean language has ten vowel phonemes that can be altered depending on their position in the word, along with 21 consonants phonemes. Different regions in Korea speak the six different dialects of the Korean language. Gangwon province found in South Korea uses The Yeongseo dialects. The Jeju dialects are spoken in Jeju Island, while the Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Incheon regions use the Seoul dialects. The Jeolla dialects are common in Jeolla and Gwangju city areas, and the southern-east Gyeongsang regions including Ulsan, Busan and Daegu cities the Gyeongsang dialects are prevalent. Many Koreans speak English or have taken English lessons in school.
Standard Korean is the language used by almost all 50 million citizens of South Korea. In addition to the native language, most people below 40 years of age use English which means over 58% of Koreans speak English frequently. One of the most prominent minority languages in South Korea is Chinese, which is spoken by over 1.2 million residents.
For visitors, despite common use of English knowing a few key phrases may make life much easier especially in rural areas or when dealing with senior citizens. To say hello one has to say “Annyeonhhaseyo”, pleased to meet you in Korean will be “Mannaseo bangawoyo.” My name is… in Korean is “Je ireum-eun.” Imnida, please will be “Butakamnida,” “Kamsahamnida” means thank you, while “mianhamnida” means sorry
Past interactions of Korea with invading countries and colonists played a significant role in shaping the linguistic landscape of Korea. A Chinese Mandarin and Cantonese speaking community are found all over Korea. Some elderly Koreans still speak Japanese, especially in the southern city of Busan.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
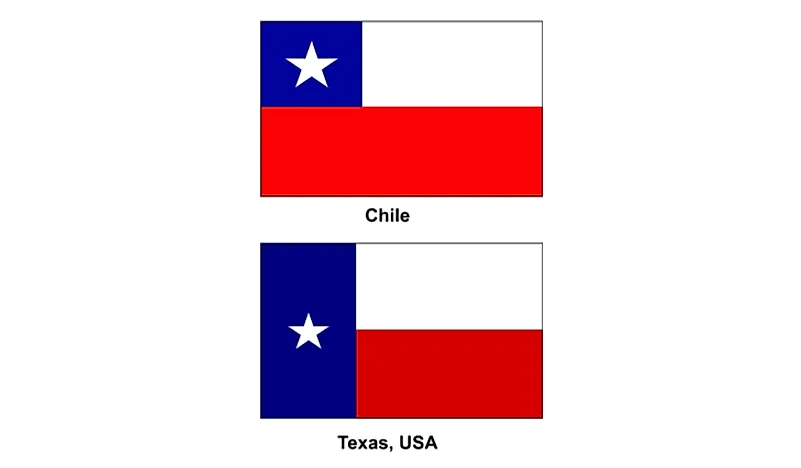
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20