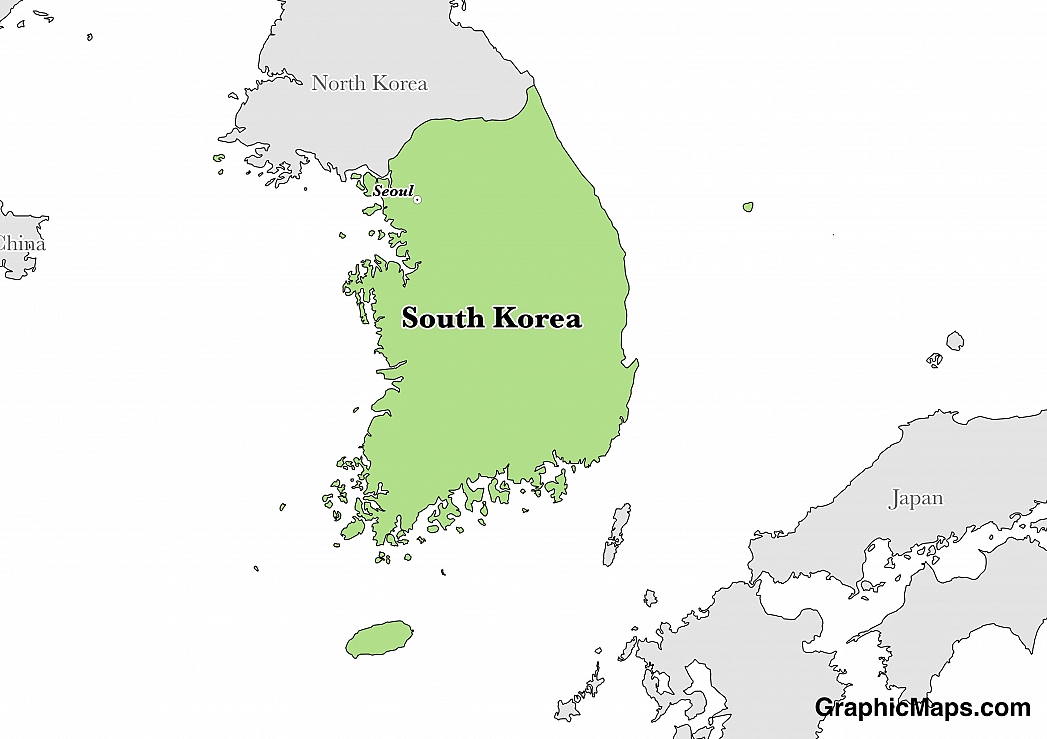
The political framework of South Korea is a presidential representative democracy, with the president as the head of state, the head of government and the commander in chief of the armed forces of South Korea. The government functions are centralized at the national level. The president is the only member of the executive team that is directly elected. The cabinet is the policy deliberation body of the executive composed of 15 to 30 members with the president as the chairperson and prime minister as the vice chair. However, the prime minister is the one who chairs cabinet meetings often. The legislative power is vested in the government and in the national assembly. The legislature is a single large unicameral 300 member assembly elected from individual constituencies. Besides the 300, 56 members are elected to the assembly through a proportional representation. The judicial arm which is independent of the executive and legislature is national and comprises of the Supreme Court, the Constitutional court, the appellate court, district court, municipal and the specialized courts. The local government, on the other hand, are autonomous units operating in their respective regions. The only exception is the mayor of Seoul who sits on the cabinet due to the unique status accorded by the city.
The National Election Commission oversees elections in the country where National Assembly members are elected after every four years, unless a member is unable to complete their term, then a by-election can be called. The president is the only one who is permitted to serve for a one five–year term, but in case the president is found guilty of wrong-doing the National Assembly can pass a motion of impeachment which if endorsed by the Constitutional court can give way for a by-election.
The South Korean Presidential official residence and office is in Jongno-gu, Seoul, located in Cheong Wa Dae, the site of the royal villa that was built by King Sukjong in 1104. The house was completed in 1991 and is named after its blue-tiled roof. The National Assembly building is situated along the Hangang River in Seoul, completed in 1975, and the grand blue domed house has 24 granite pillars symbolic of the diverse public opinions that merge as one.
The Republic of South Korea is a multi-party democracy. The country currently has two major parties that emerged after the 2017 elections - these parties are the Democratic Party of Korea (DPK) and the conservative Liberty Korea Party (LPK)/ The other significant minor parties with house representatives are Centrist People's Party, the Liberal-Conservative Party, and the Progressive Justice Party. The political sphere in South Korea is dynamic, and almost all parties have transformed by merger or renaming. For instance, the leading party of the DPK was formerly known as Minjoo Party of Korea which before that was called New Politics Alliance for Democracy that was a result of a merger between the New Political Vision Party and The Democratic Party.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
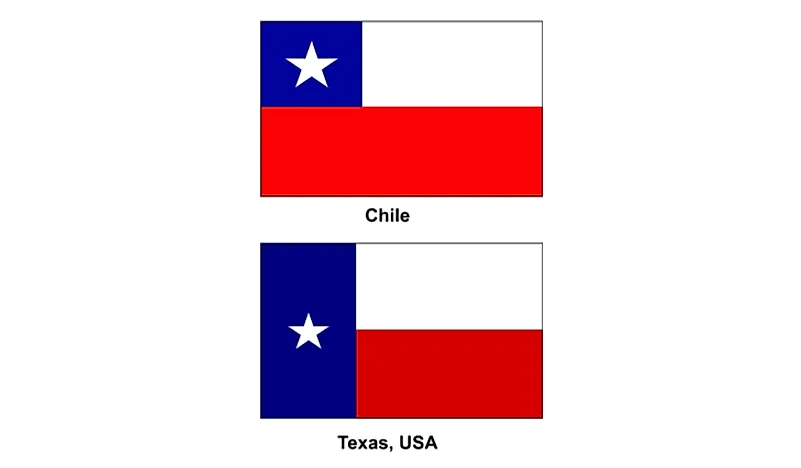
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20