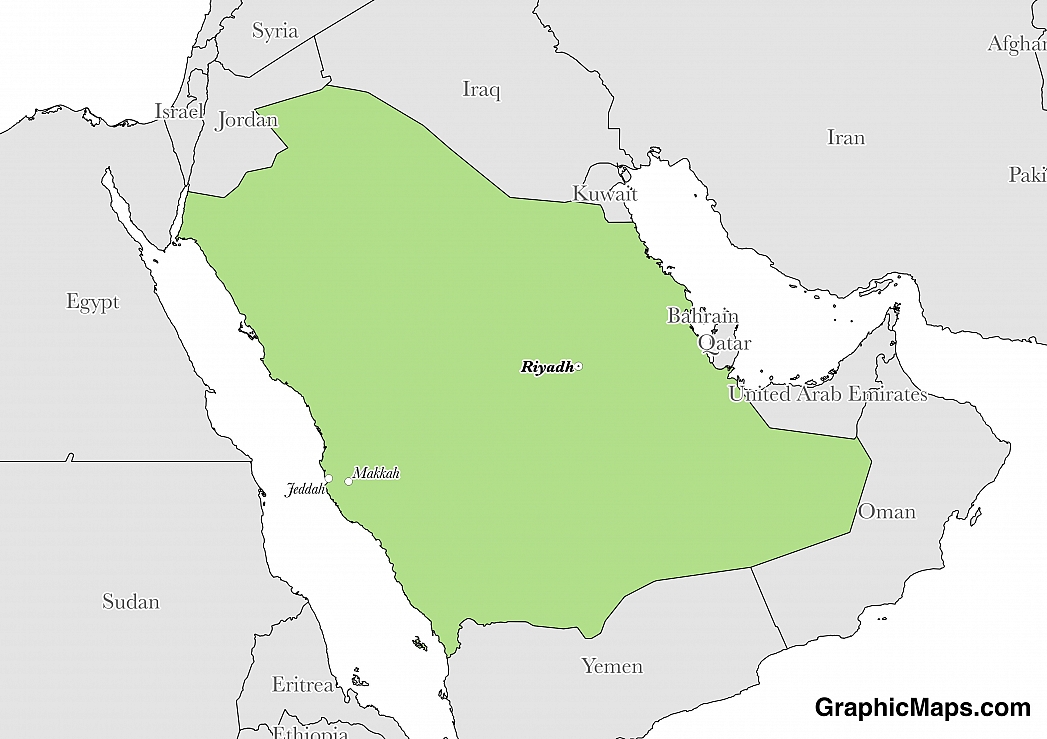
Saudi Arabia's government functions with two different arenas. Political matters are conducted within the Saudi royal family, and between the Saudi royal family and the rest of the society within Saudi Arabia. However, even with the latter, this is often limited to a small number of people. Tribal sheikhs, people who are very powerful in the commercial sector, and the ulama are the people outside of the royal family who get most participation in politics. Tribal identity is strong in Saudi Arabia, and for this reason, it plays a role in politics.
There are no national elections in Saudi Arabia. The King of Saudi Arabia inherits his position of power. There is no vote on who is the king. In other monarchies, there is a vote on who the Prime Minister will be. This is the case for countries such as The Netherlands, United Kingdom, Belgium, Japan, Sweden, and Thailand. This is not the case for Saudi Arabia. No Prime Minister or President is elected. The king is more than a figurehead in Saudi Arabia. He serves the same role that a Prime Minister would serve in constitutional monarchies, plus having more powers. In places where a President or Prime Minister are elected, the head of state has control over the executive branch of government. In Saudi Arabia, the king is in charge of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the government. The government of Saudi Arabia is ruled by the royal family. Decisions for the public policy are made with the consideration and consultation of the royal family.
The King's Palace is the official residence of the king of Saudi Arabia.
With the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia being an absolute monarchy, no political parties are allowed to exist.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
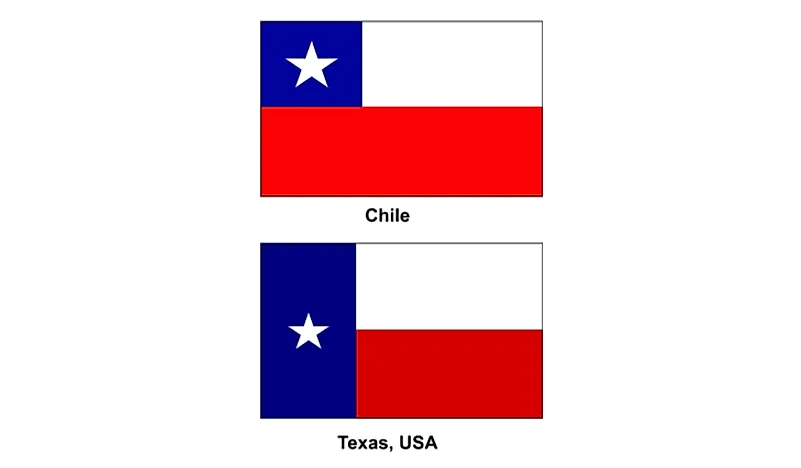
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20