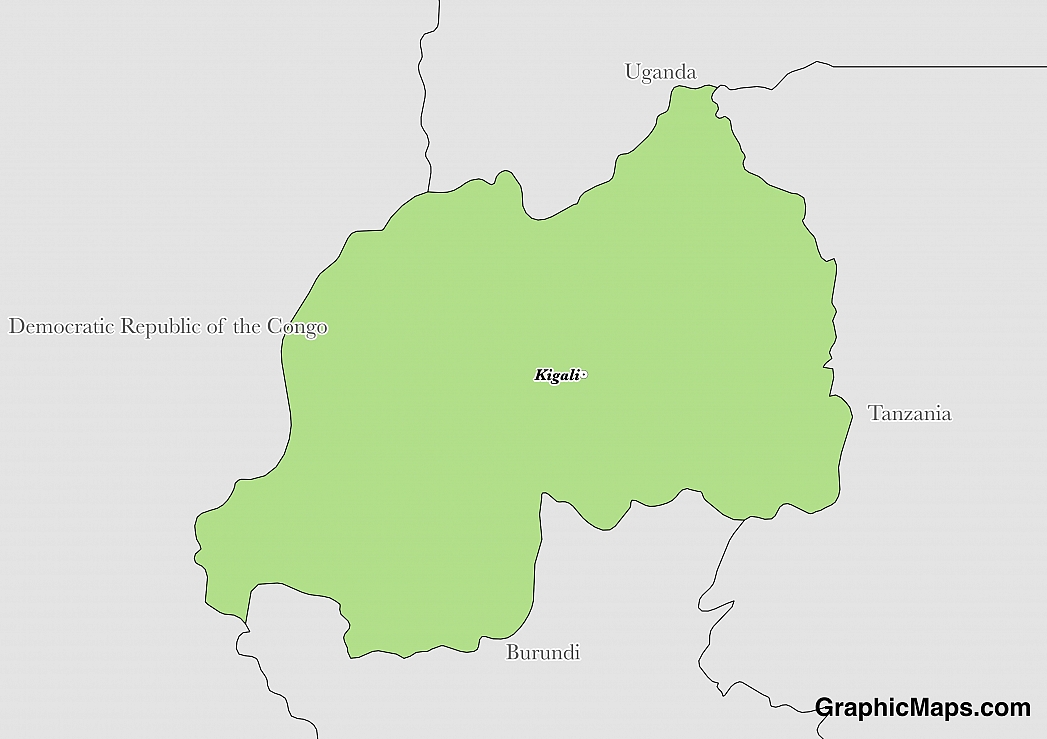
The political system of Rwanda is considered a Presidential Republic with elements of Belgian and German systems of civil law due to colonial ties. The President of Rwanda is the head of government and head of state within a multi-party system. Executive power is held by the government and legislative power is vested in the parliament of Rwanda. Elements of both the 1991 Constitution of Rwanda and the 1993 Arusha Peace Accords made their way into the 2003 Constitution of Rwanda.
Elections for the Presidency of Rwanda are held every seven years. The members of the Senate are elected or appointed for eight-year terms and 12 are elected, eight are appointed by the President, four appointed by the Forum of Political Parties, and two appointed by university staff. Of the 80 seats in the Chamber of Deputies, 53 are elected directly by the citizens of Rwanda, 24 elected indirectly by provincial councils, and the remaining three are appointed by the National Youth Council and the Federation of the Associations of the Disabled.
The parliament of Rwanda is divided into two chambers, the Senate, and the Chamber of Deputies. This parliament is located in the capital city of Kigali which is slightly east of the centre of the country. The Chamber of Deputies was created in 2003 and adopted by referendum the same year. The parliament has also focused on the economic development of Rwanda and is considered a positive force for change in a country that has had a troubled past.
There is only one political party that dominates politics in Rwanda. It is the Rwandan Patriotic Front.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
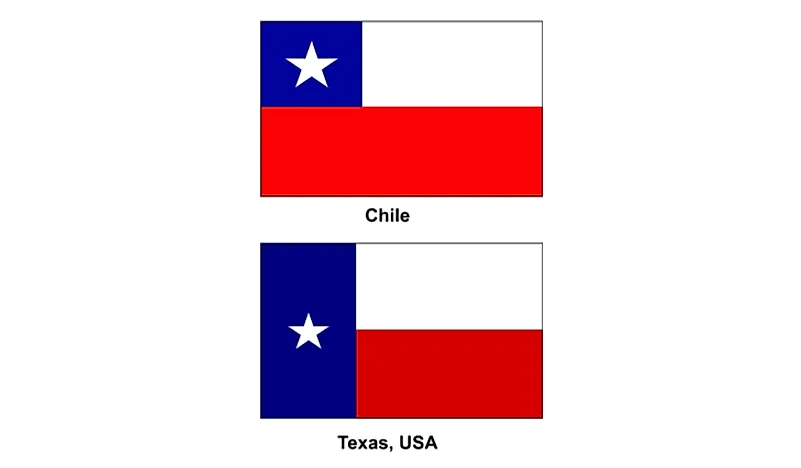
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20