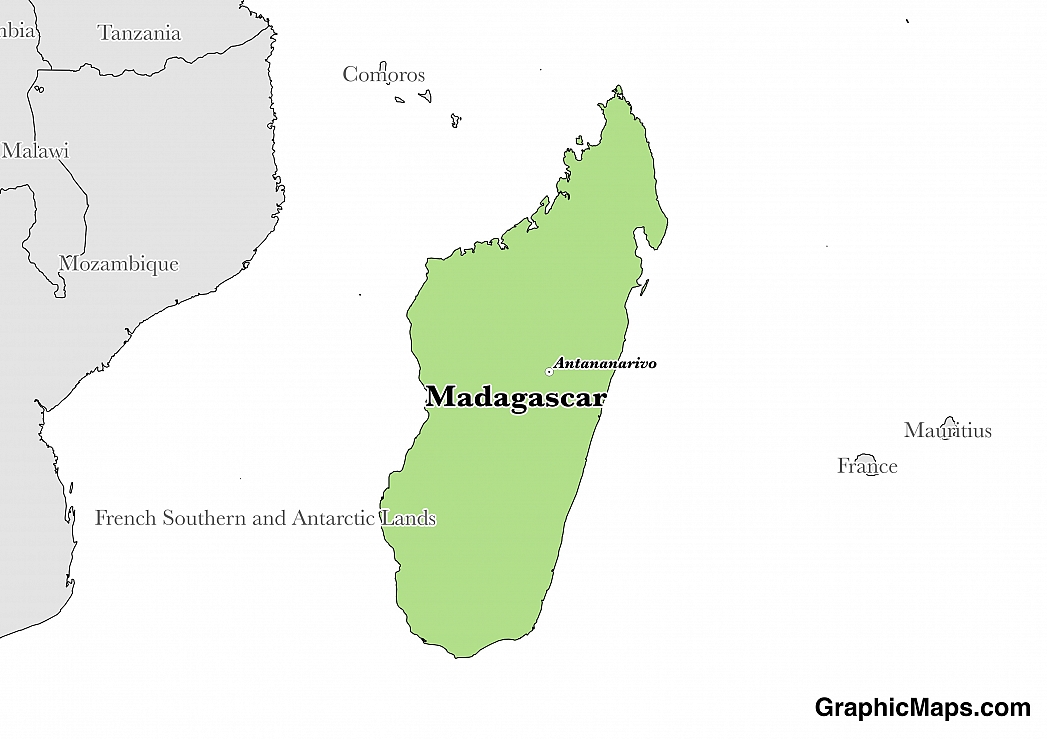
Malagasy and French are the two official languages of Madagascar according to the 1958 constitution. French is spoken in Madagascar because it was once a French colony. The revised 1992 constitution did not indicate any languages but the constitution of 2007 named Malagasy as the national language while French and English are the official languages. In 2010 with a majority vote by the people, English was eliminated as an official language. The Malagasy language is classified under the Austronesian group of languages. The Malagasy alphabet contains 26 letters. The language adopts some words from Arabic and the Sabaki languages, and lately there have been a few borrowed words from French and English. Written Malagasy dates back to the 15th century.
Malagasy is divided into two main local languages, the Western which comprises sakalava, and Eastern comprising of Merina. The two languages are differentiated in pronunciation. The languages are further classified into 12. On the Eastern side, there is Northern Betsimisaraka Malagasy which is spoken by 1.2 million of the Betsimisaraka people living in the Northeastern part of the island. Southern Betsimarakasa Malagasy is spoken in the Southeastern region by about 2 million people. Plateau Malagasy is spoken in central Madagascar by about 7.5 million people. Tanosy Malagasy is used by the Antanosy ethnic group, while the Tesaka Malagasy is spoken by about 1.1 million people of the Antaisaca population. The Western side is grouped into Antankarana Malagasy spoken by the Antankarana in the North of the island. Bara Malagasy has around 724,000 speakers who are the Bara. Masikoro Malagasy has about 550,000 speakers of the Masikoro language. Sakalava Malagasy is spoken by around 1.2 million people. Tandroy-Mahafaly Malagasy has about1.3 million speakers of the Antandroy and Mahafaly people. Tsimihety Malagasy has approximately 1.6 million speakers who fall in the Tsimihety ethnic group. Bushi has about 41,700 speakers and is common in the French-administered island of Mayotte.
Some of the useful phrases in Malagasy language include “eny” which means yes, “manao ahoana” which means hello or how are you,“veloma” meaninh goodbye, and “azafady” meaning please.
Apart from the subgroups of the Malagasy language, Madagascar does not have any other minority languages. English and French are foreign languages widely used by the majority of the population for official communication. The subgroups of the Malagasy language are considered local dialects with Merina Malagasy used as the standard Malagasy understood by all the subgroups.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
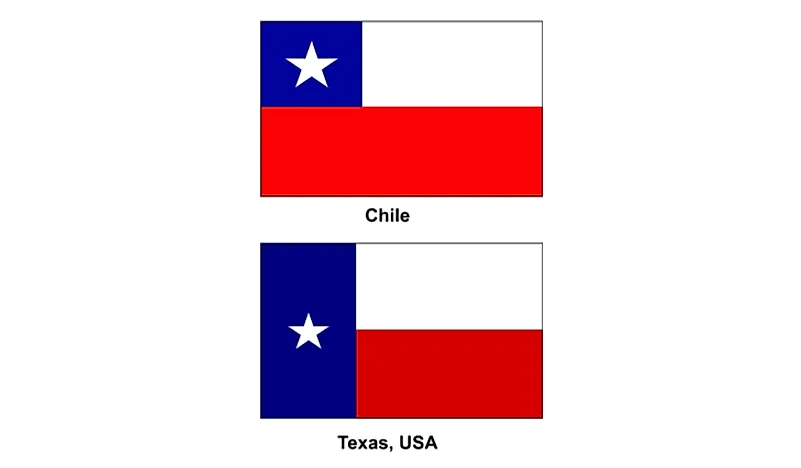
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20