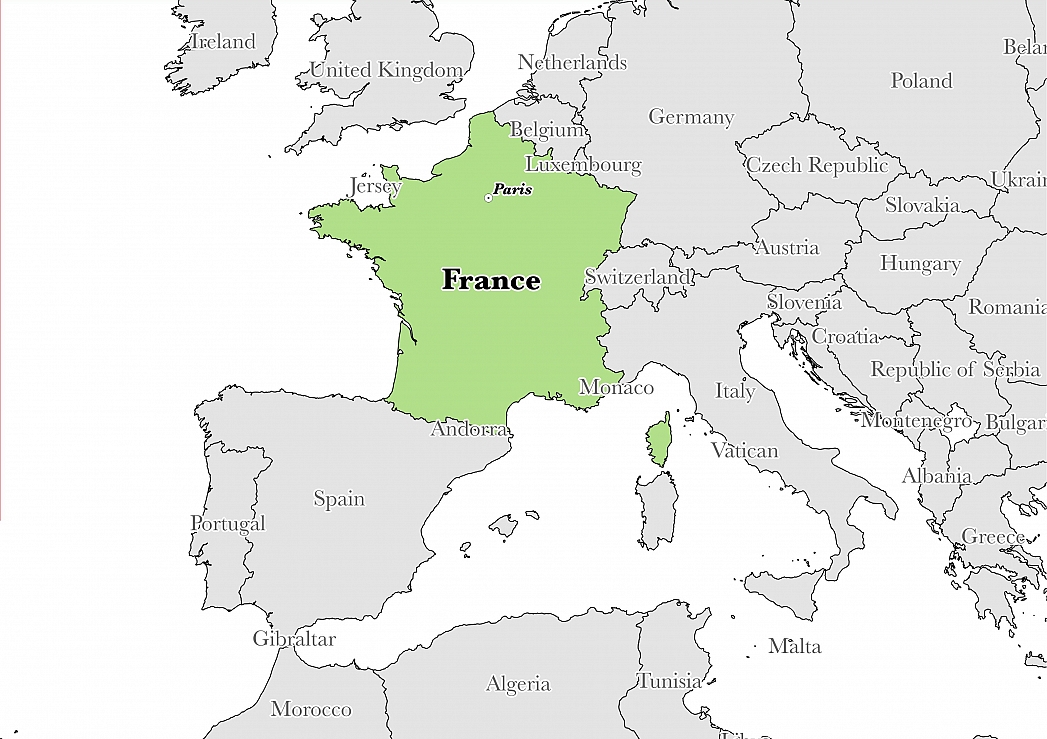
The Fifth Republic is the current system of government in France. It is based on the Constitution of the Fifth Republic which was adopted in 1958, after the Fourth Republic collapsed, under the leadership of Charles de Gaulle. It is a semi-presidential representative democracy, where the Head of State is the President. The Executive comprises of the President and the Government which in turn is made up of the Prime Minister who is also the Head of Government and the Ministers. The Parliament is the legislative branch, and it is made up of two houses, that is, the National Assembly which is the principal legislative body and the Senate, while the Judiciary is separate and independent.
French citizens directly elect the President of France as well as the 577 members of the National Assembly for five-year terms. However, the President is only eligible to serve for two terms. An electoral college made up of locally elected representatives elects the 348 members of the Senate. The office of Prime Minister is appointed by the President. However, if his political side does not control a majority in the National Assembly, his appointee has to reflect the majority. The Prime Minister has no fixed term and stays in office for as long as he has the goodwill of the President and National Assembly.
The National Assembly meets in the Palais Bourbon in Paris on the bank of the River Seine. The construction of started in 1722 as a country house, but was nationalized during the French Revolution, and later in 1806 Napoleon made modification to mirror the church of Madeleine. On the other hand, the Senate meets at the Palais du Luxembourg which is located in the 6th Arrondissement of Paris. The President and the Prime Minister reside in the Palais de l’ Élysée and the Hôtel Matignon respectively. All these buildings previously belonged to the aristocracy but were nationalized and converted for government use after the French Revolution.
Political parties in France are generally organized by right-wing parties (the National Front, the Union For the Popular Movement), centrist parties (Democratic Movement, New Centre), and left-wing parties (Socialist Party, Unitarian Left).
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
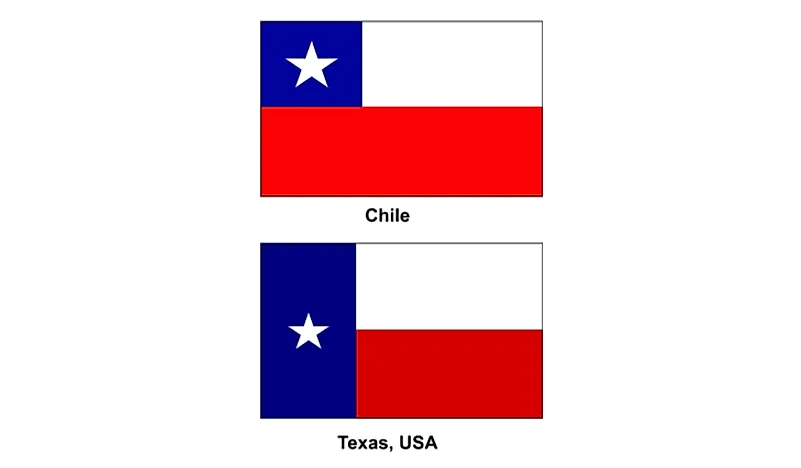
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20