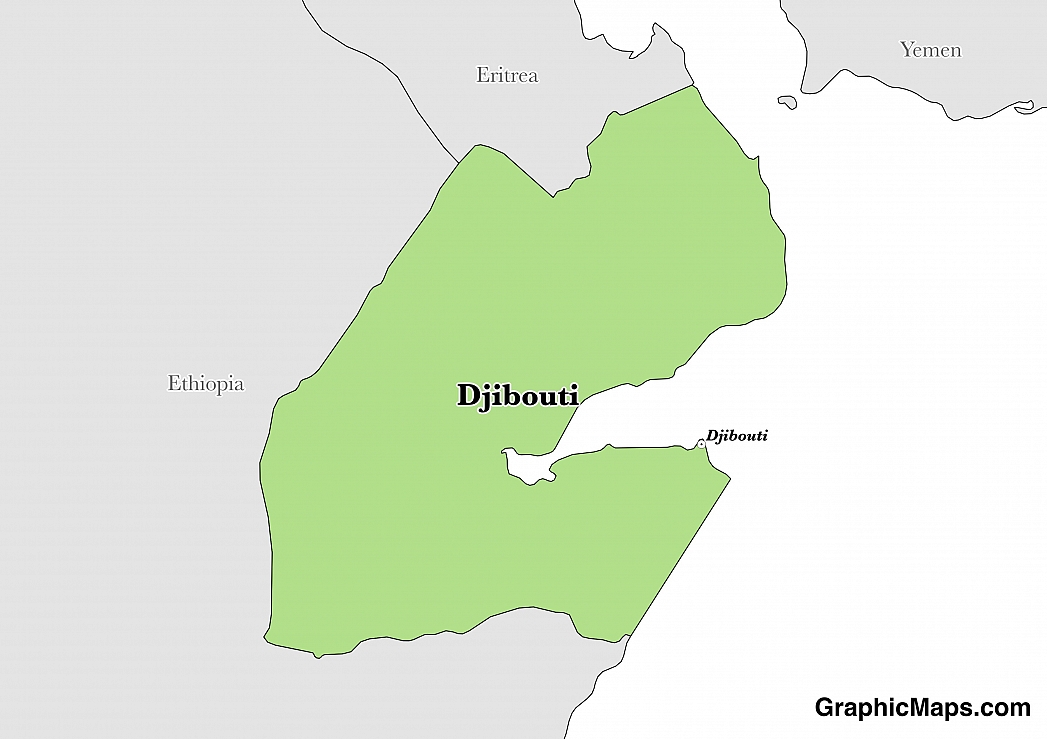
Official languages of the country are Arabic (an Afro-Asiatic language) and French (Indo-European). French has been inherited from the nation's colonial past and Arabic has important cultural, religious, and societal roots. Djibouti is considered a bi-lingual nation with many important signs and announcements in both Arabic and French as well as regional dialects where applicable.
Although they are not considered official languages, Somali and Afar are the most widely spoken with approximately 88% of the country speaking either of these dialects. Somali has over 520,000 speakers in Djibouti and Afar has just over 300,000. Just 17,000 native Djibouti citizens speak French as a first language and 59,000 speak Arabic as their native tongue.
Although many in the country understand English, Arabic and French phrases will also be useful in Djibouti. "As-salaam alaykum" is a common Arabic phrase meaning “peace be unto you”, and be used as a greeting in any situation. The correct response to this phrase is “wa alaykum as-salam” which means, “and unto you, peace”. The phrase “shuk-ran”, means thank-you, and excuse me is pronounced "af-wan". Hello, written as bonjour and pronounced as "bon-jour" is a very common greeting in any society that speaks French. "Mer-ci" is also an easy word to learn and it means thank-you.
Minority languages in Djibouti include the Amharic, Oromo, and Ta'izzi-Adeni Arabic dialects, an example of the languages that migrants have brought to the country. There are also small communities of Greek and Hindi speakers. The main foreign language of Djibouti is English and many schools now teach English as a mandatory subject. This will contribute greatly to the assimilation of Djibouti to the global community in future years.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
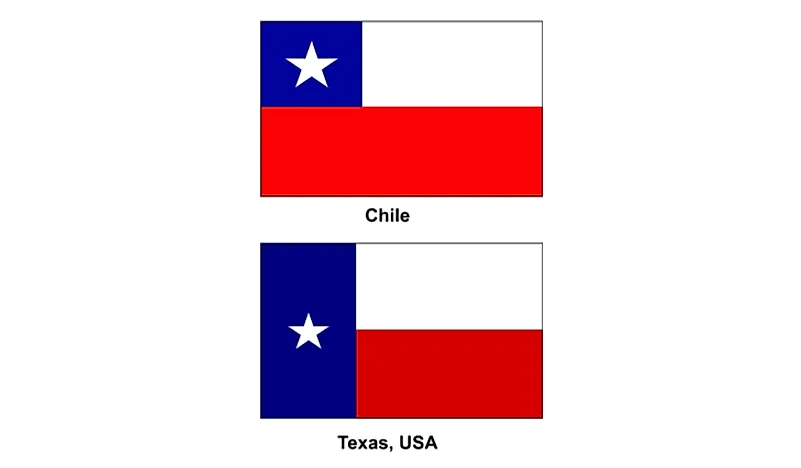
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20