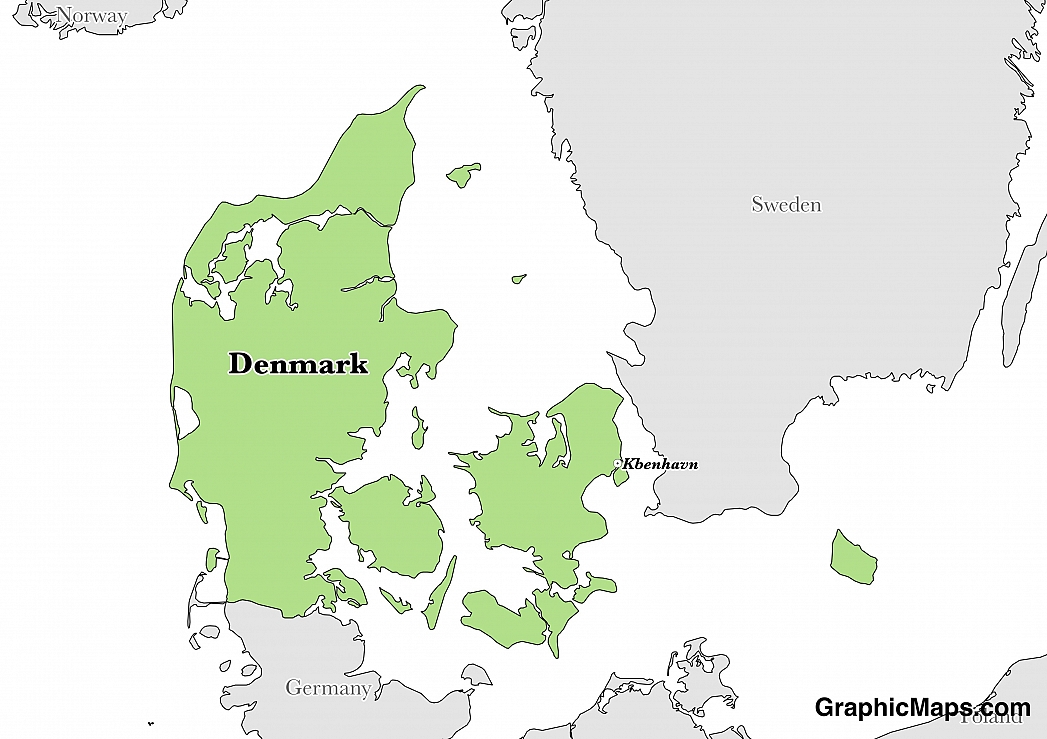
Although there are many languages spoken in Denmark, the official and state language is Danish. It is a North Germanic dialect that is used by about 6 million individuals, mainly Danes. Danish is among the three main Scandinavian languages. There are 29 letters in the Danish alphabet, 26 of which are used in the English alphabet, along with three additional vowels at the end. These three added vowels are Æ, Ø, and Å. At the regional level, inhabitants of the Faroe Islands, a self-governing area, speak Faroese. Greenland, an equally self-governing zone of Denmark speaks Greenlandic.
The three Scandinavian languages of Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish are closely related. A native speaker of one of these languages might understand the other two to some degree. However, Danish is unique from the other two essentially because there is a large incongruence between written and verbalized language. For example, the written “af’’ sounds like “ow.” Verbally, the words are condensed, and the consonants softened.
Danish can be a difficult language to learn, but knowing a few simple phrases can go a long way. In Danish, "Velkommen" means "welcome", and "hej" means "hello". To say "how are you?" one would say "hvordan har du det?"
Besides Danish being the official regional language, there are other minority languages used in Denmark, including German. It is the formal minority language of a group of people living in the region of Southern Denmark, previously known as the South Jutland County. This population of German minority also runs their primary schools where German is the main language used to teach. English is another minority language spoken by a majority of Danes as a second dialect. The language is compulsory for Danes and is taught until the fifth grade after which it becomes optional. Swedish is also a minority language spoken in Denmark.
This page was last modified on May 1st, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
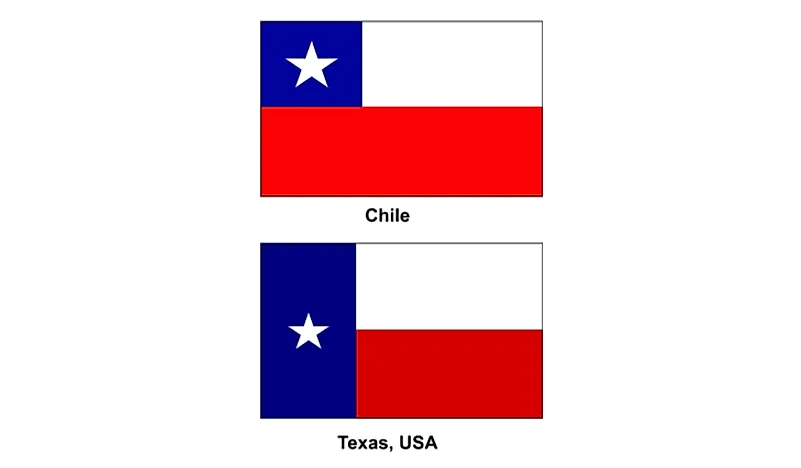
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20