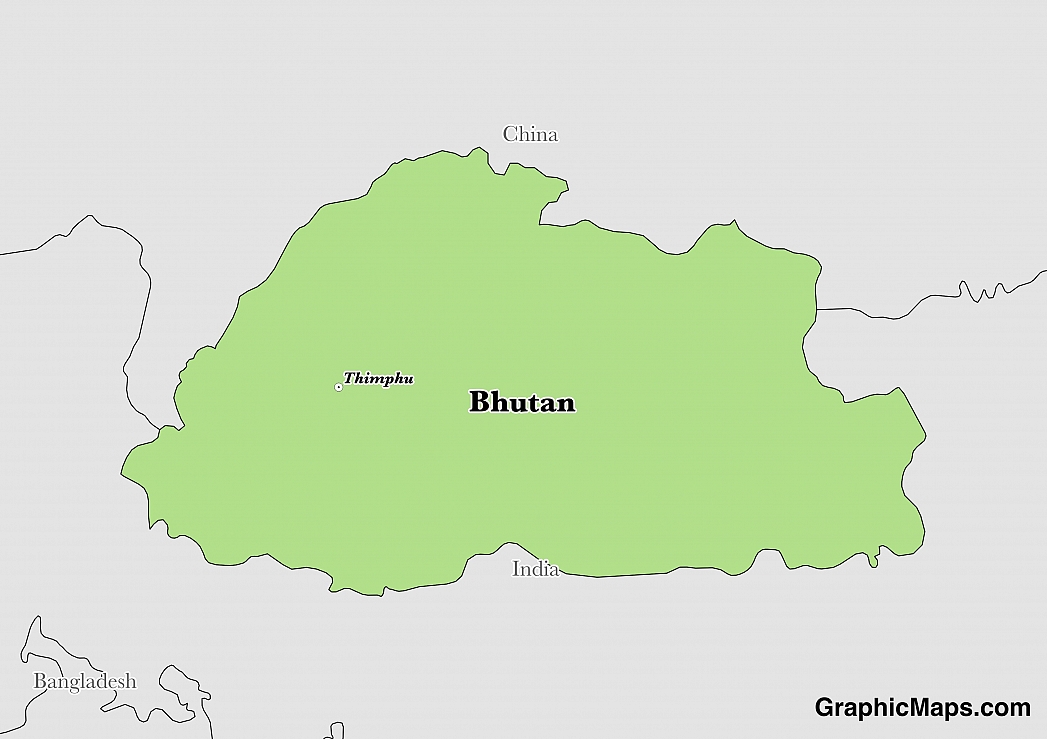
Where is Bhutan?
Located in Southern Asia, Bhutan has a 1,136.00 km border with China (477 km) and India (659 km). Bhutan and China are currently still involved in negotiations to establish a common boundary alignment.
The capital of Bhutan is Thimphu, located in Thimphu District near the Raidak River. The city became the capital following a royal declaration of 1961 and remains the only city in the country. Thimphu’s population is slightly more than 100,000 and a population density of slightly less than 7,8500 people per square mile. The city’s population density is highest in the country and continues to witness an increase in the number of people. This city relies majorly on the historical buildings for tourist attractions although the government is careful not to prioritize the sector to an extent that it overshadows the other economic development programs. Thimphu has a subtropical highland climate that is heavily influenced by monsoon winds. June to December constitute the wettest months while the other months are relatively dry.
Read more on Bhutan's CapitalBhutan is an Asian country covering 38,394.00 km2. This makes it the 62nd smallest country in the world and slightly larger than Maryland; about one-half the size of Indiana. Its geographic coordinates are 27 30 N, 90 30 E and Thimphu is the capital city.
The countryis named after Bhotia, the ethnic Tibetans who migrated from Tibet to Bhutan.
Its ISO code is BT.
Geography
Bhutan has a mean elevation of 2,220 m above sea level.
It has a climate that is mostly tropical in the southern plains, and less moderate in the central valley and Himilaya regions. Its terrain is mostly mountainous with some areas of savanna.
Population
Bhutan has a population of 750,125 making it the 164th largest in the world.
Sharchhopka, Dzongkha, Lhotshamkha are all widely spoken. The major ethnicities are Ngalop, ethnic Nepalese and indigenous or migrant tribes. The population is mostly Lamaistic Buddhist.
Since 1971, the official and most spoken language of Bhutan has been Dzongkha. Dzongkha is a member of the Siro-Tibetan language group and uses the 30 letters of Tibetan alphabet. This language, in written form, is segmented with no vowels but some consonants assume an inherent vowel. Dzongkha is native to western Bhutan but spoken as a second language in the other regions. In total, more than 600,000 people speak the language. Some useful phrases for first timers and non-speakers are like Kuzoozangpo La, Nga America ley ein, and Atsi zur nang and others. Linguistically, Bhutan is diverse with many languages of Tibetan, East-Bodish, Tibeto-Burman, and Indo-Aryan origins.
Read more on Bhutan's LanguagesThe dialing code for the country is 975.
Government
Bhutan is an independent country. It became a unified kingdom in 1907. Its constitution was last ratified in 2008.
Bhutan moved from absolute monarchy to constitutional monarchy in 2008 and, currently, the king is the head of state and prime minister the head of government. Executive powers rest on the cabinet while parliament has legislative powers. The King’s official palace is Dechencholing Palace, built in 1953 in the capital’s CBD. However, the current King resides in the Wangdichholing Palace built in the mid-1800s, the birthplace of the first King’s father. Elections in Bhutan is through suffrage where each representative has a constituency. The electoral commission has laid down elaborate guidelines for successful elections. Unique to this country is that the king has an age limit and can also be voted out by parliament.
Read more on Bhutan's GovernmentEconomy
Factoring in Purchasing Power Parity, Bhutan's GDP is $6,432,000,000.00 (USD) with $8,100.00 (USD) per capita. This makes it the 165th largest economy and its citizens the 146th richest in the world. The currency of Bhutan is the Ngultrum (BTN).
Its major export partner is India. Its main exports are electricity, ferrosilicon, cement, and cardamom. Its major import partners are India and France. Its major imports include fuel, lubricants, airplanes, and machiney.
Flag
Bhutan has a rectangular flag of two colors, yellow and orange, divided by a diagonal line and the Druk dragon spread at the center facing the fly side while holding four jewels. The colors and symbols of this flag represent the country’s ties with its traditional beliefs, kingdom, government, and its wealth in a modern world. Mayeum Choying designed the first known flag that closely resembles the current one although, over the years, changes have been made to make it more appropriate to the country. These changes include the color of the background and the dragon as well as the measurements and direction of the dragon.
Read more on Bhutan's FlagThis page was last modified on January 17th, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
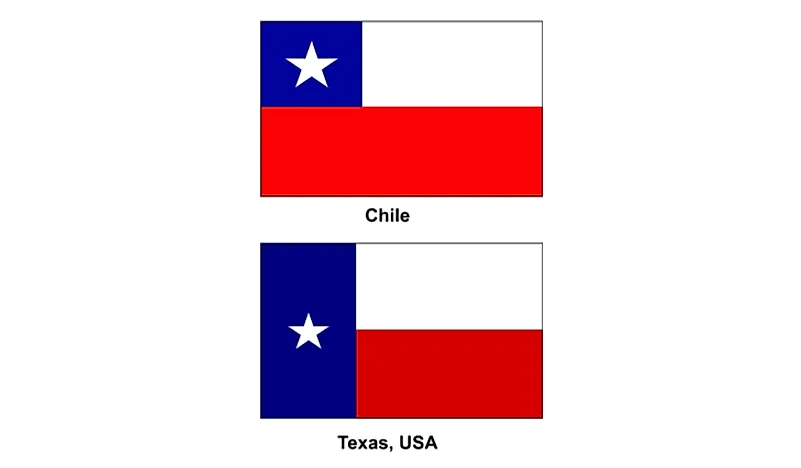
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20