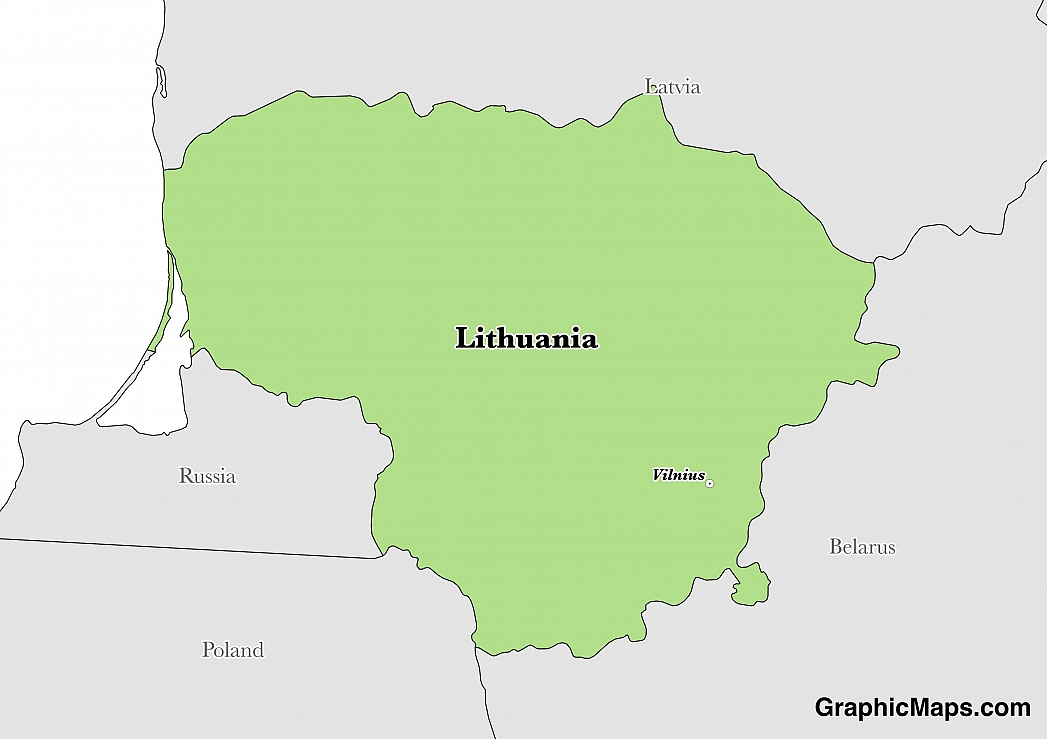
Where is Lithuania?
Located in Eastern Europe, Lithuania has a 1,549.00 km border with Belarus (640 km), Latvia (544 km), Poland (104 km), Russia (Kaliningrad) (261 km). It has a 90.00 km coastline. Lithuania and Russia committed to demarcating their boundary in 2006.
Vilnius is the capital city of Lithuania. It is located in the south-eastern region of Lithuania and experiences a humid continental climate with July and January as the hottest and coldest months respectively. It is the major economic center in Lithuania. It was first the capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 1300s. Vilnius was recognized as Lithuania’s capital city in 1922. It also hosts most of the government offices, cultural heritage centers, schools, religious centers, museums, and parks. Vilnius has a population of approximately 542,000 individuals, with the demographic trends characterized by a decline. The town has a unique architecture which led to its listing as a World Heritage Site in 1994.
Read more on Lithuania's CapitalLithuania is a European country covering 65,300.00 km2 of which 4.01% is water and 62,680.00 km2 is land. This makes it the 74th smallest country in the world and slightly larger than West Virginia. Its geographic coordinates are 56 00 N, 24 00 E and Vilnius is the capital city.
The meaning of the name "Lietuva" remains unclear, although it may be named for a stream in east central Lithuania.
Its ISO code is LT.
Geography
Lithuania has a mean elevation of 110 m above sea level.
It has a transitional climate with wet, moderate winters and summers. Its terrain is mostly made up of lowlands with many scattered small lakes and fertile soil.
Population
Lithuania has a population of 2,854,235 making it the 140th largest in the world. The country has a fairly evenly distributed population.
Lithuanian is the official language; Russian and Polish are also widely spoken. The majority ethnic group is Lithuanian. The majority of the population is Roman Catholic.
Lithuanian is the official language of Lithuania. It is used in government and other official institutions. It is one of the surviving Proto-Indo languages. The language is very conservative. It has therefore retained some features that have been abandoned by related languages. Other common languages used in Lithuania are Polish, Russian, and Ukrainian. The younger population is more fluent in English, which is offered as a subject in most schools as a foreign language. Lithuanian has also been borrowing words from other languages to enrich its vocabulary.
Read more on Lithuania's LanguagesThe dialing code for the country is 370.
Government
Lithuania is an independent country. It declared its independence in 1990. Its constitution was last ratified in 1992.
Lithuania is a representative democracy state. The president is elected every five years and can only serve for a maximum of two terms. The president appoints the prime minister who is in charge of the government. The parliamentary house is called the Seimas, located at the center of Vilnius. The residence of the president, also commonly referred to as the Presidential palace is located in old town of Vilnius. Eligible voters elect the members of parliament, the president, mayors, and delegates of the European Parliament. Voting is by secret ballot method. The elections are conducted by the Central Electoral Observers.
Read more on Lithuania's GovernmentEconomy
Factoring in Purchasing Power Parity, Lithuania's GDP is $85,620,000,000.00 (USD) with $29,900.00 (USD) per capita. This makes it the 89th largest economy and its citizens the 60th richest in the world. The currency of Lithuania is the Litas (LTL).
Its major export partners are Russia, Latvia, and Poland. Its main exports are refined fuel, machinery and equipment, and chemicals. Its major import partners are Russia, Germany, and Poland. Its major imports include oil, natural gas, machinery and equipment.
Flag
The tricolored flag of Lithuania has been in use since 1918 with the exception of periods of Soviet and Nazi control. The flag comprises of the colors of red, yellow, and green. The yellow color signifies Lithuania’s prosperity while the green color symbolizes the environment and natural resources. The red color stands for the sacrifice and lives lost during the struggle for independence. Between the 16th century and early 20th century, Lithuania had a red colored flag with a white knight riding on a horse. The previous flag was initially used as a banner and was only made the country’s official flag in 1905. The current flag was designed by a team of three men including Antanas, Tadas, and Basanavicius.
Read more on Lithuania's FlagThis page was last modified on January 17th, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
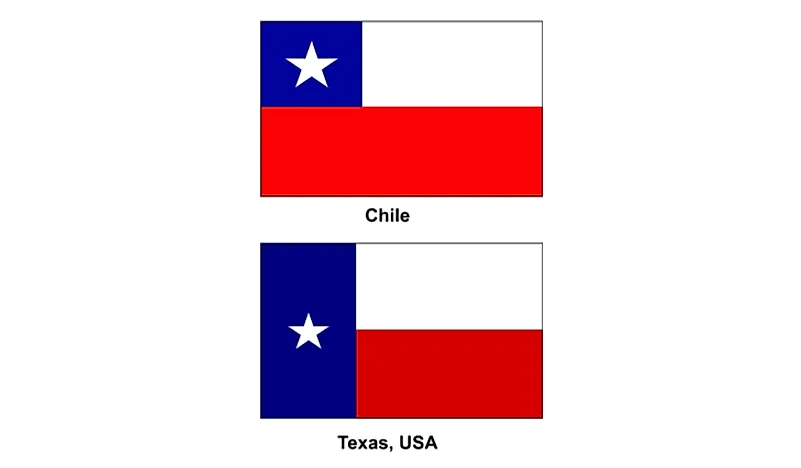
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20